How to Install Git on Linux, Ubuntu, CentOS, Mint, Fedora?
This tutorial includes the commands to install Git on Linux- Ubuntu 12.04, 13.04, 14.04, 15.04, 16.04, CentOS, Mint Linux , Fedora, Red Hat, Arch Linux- Kernel. An indispensable tool in modern software development is some kind of version control system. Version control systems allow you to keep track of your software at the source level. You can track changes, revert to previous stages, and branch to create alternate versions of files and directories.
One of the most popular version control systems is git, a distributed version control system. Many projects maintain their files in a git repository, and sites like GitHub and Bitbucket have made sharing and contributing to code simple and valuable.
In this tutorial guide, I will demonstrate how to install git on an Ubuntu 14.04 VPS instance. I will cover how to install the software in two different ways, each of which have benefits.
How To Install Git with Apt-
By far the easiest way of getting git installed and ready to use is by using Ubuntu's default repositories. This is the fastest method, but the version may be older than the newest version. If you need the latest release, consider following the steps to compile
git from source.
You can use the
apt package management tools to update your local package index. Afterwards, you can download and install the program.
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install git
This will download and install
git to your system. You will still have to complete the configuration steps that we cover in the "setup" section.How To Set Up Git-
Now that you have
git installed, you need to do a few things so that the commit messages that will be generated for you will contain your correct information.
The easiest way of doing this is through the
git config command. Specifically, we need to provide our name and email address because git embeds this information into each commit we do. We can go ahead and add this information by typing:
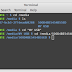
$ git config --global user.name "Your Name"
$ git config --global user.email "youremail@domain.com"
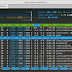
We can see all of the configuration items that have been set by typing:
$ git config --list
As you can see, this has a slightly different format. The information is stored in the configuration file, which you can optionally edit by hand with your text editor like this:
$ nano ~/.gitconfig
There are many other options that you can set, but these are the two essential ones needed.
This makes more work for you because you will then have to revise the commits you have done with the corrected information.